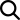Taxes for UK Business Owners: 2019/20 Tax Rates, Thresholds & Allowances
Small business owners face double responsibility when paying taxes: they account both for themselves and for their companies. It is tiresome to keep up with the shifting tax rates, tax bands and allowances, so here is a guide for a private limited company owner to survive the 2019/2020 tax year.
Below you will find the tax rates and thresholds for 2019/20 as well as brief explanations of what is what. This article is enough for you to make informed decisions, but we recommend entrusting the filings to a certified bookkeeping services provider.
Personal tax rates
Here we explain how personal allowance works, how much income tax a person is to pay depending on the earnings and what else is affected by the income you have over the tax year. Spoiler: the more money you make, the higher rates you are subject to. This works for dividend tax, capital gains tax, and even national insurance contributions.
Personal Allowance
The Personal Allowance (“tax-free allowance”) is the amount of money you can earn during a tax year without paying Income Tax on it. For example, during the tax year 2019/20, you will pay zero tax on the first £12,500.
And what if you earn more than that? What if you make, say, £92,500? Then £12,500 of these won’t be taken into consideration when calculating your Income Tax, and your taxable income will be £77,500. Neat!
The deduction thing applies until you earn more than £100,000 within a tax year. This threshold is called the Income Limit for Personal Allowance. After you pass the £100,000 mark, the sum you don’t get taxed for starts shrinking. For example, you earn £120,000. This means you earn £20,000 more than the Income Limit for Personal Allowance. 50% of those £20,000 will be deducted from your Personal Allowance:
£12,500 – £10,000 = £2,500
Thus, you won’t pay taxes on £2,500 of your income. Mind that you do not get a Personal Allowance on taxable income over £125,000.
| Personal Allowance Threshold | Sum |
|---|---|
| Personal Allowance | £12,500 |
| Income limit for Personal Allowance | £100,000 |
Income Tax rates and tax thresholds
There are three rates: the basic one, the higher one, and the additional one. The more you make, the higher your income tax rate will apply.
| Taxable income | Tax rate | How much you pay |
|---|---|---|
| Up to £12,500 | — | 0% |
| £12,501 to £50,000 | Basic rate | 20% |
| £50,001 to £150,000 | Higher rate | 40% |
| over £150,000 | Additional rate | 45% |
Dividend tax rates
There is a tax-free dividend allowance: if you receive less than £2,000 in dividends, you don’t pay tax on them.
Those who make more than £2,000 have to pay. The more money they make, the higher the rate is.
| Taxable income | Income Tax rate | How much you pay on dividends |
|---|---|---|
| Up to £12,500 | — | 0% |
| £12,501 to £50,000 | Basic rate | 7.5% |
| £50,001 to £150,000 | Higher rate | 32.5% |
| over £150,000 | Additional rate | 38.1% |
National Insurance rates
You must pay National Insurance if you’re 16 and:
- you are an employee earning above £166 a week
OR
- you are self-employed and make a profit of £6,365 or more a year
National Insurance bands and rates are different for employees, sole traders, and limited company directors.
Employee’s & Employer’s National Insurance Contributions (NIC)
Both the person and his employer pay the National Insurance contributions for the employee. However, it’s the employer’s responsibility to calculate his workers’ NIC and pay them.
The employer does not pay the contributions if the employee earns less than £166 a week. If the salary is above this threshold, the employer is obliged to pay NICs that make 13.8% of the employee’s earnings.
The employees’ National Insurance contributions (NICs) are usually calculated weekly, not annually, so that’s how we presented them in the scheme below.
Self-employed National Insurance contributions
For sole traders, there are earnings thresholds and classes of NICs. The classes mean a certain sum you must pay, the thresholds determine how much classes apply to you. Fret not, it’s easier than it sounds.
| The name of the threshold | 2019/20 |
|---|---|
| Small profits threshold | £6,365 |
| Lower Profits Limit | £8,632 |
| Upper Profits Limit | £50,000 |
So, if you earn less than £6,365 a year, you don’t have to pay NIC.
If you earn more than that, Class 2 NICs are applied: you are to pay a fixed rate of £3 per week (£156 a year).
If your sole trader business brings you £8,632 a year or more, Class 4 NICs are applied. Thus, you are to pay:
- 9% on profits between £8,632 and £50,000
- 2% on profits over £50,000.
Tadaa! Easy.
| Yearly Income | NIC Class Applied |
|---|---|
| £0—£6,365 | None |
| £6,365—£8,632 | Class 2: £3 a week (£156 a year) |
| £8,632—£50,000 | Class 2: £3 a week (£156 a year); Class 4: 9% on £8,632—£50,000 & 2% on profits over £50,000 |
Capital Gains Tax
Capital Gains Tax is a tax on the profit made when you sell something at a higher price than you originally paid. The state expects you to pay the tax when you dispose of:
- Personal possessions worth £6,000 and more
- Property that’s not your main home
- Your main home if you’ve let it out, used it for business or it’s very large
- Shares that are not in an ISA or PEP
- Business assets
Mind that it is only the gain you make that is taxed, not the full amount of money you receive from the buyer.
Every year you can enjoy an exemption from capital gains. In 2019/20, it makes £12,000. When you exceed this limit and start paying the tax, the rate will depend on your income.
| Your Taxable Income | The Income Tax Rate | Gains from Residential Property | Gains from Other Assets |
|---|---|---|---|
| £12,501 to £50,000 | Basic rate (20%) | 18% | 10% |
| £50,000 to £150,000 | Higher rate (40%) | 28% | 20% |
| over £150,000 | Additional rate (45%) | 28% | 20% |
Company tax rates
It’s possible that your business doesn’t have to deal with all the taxes and allowances listed below. The only one we can be sure about is Corporation tax. As for VAT, there are companies that have yet to register for it, which they are only obliged to do after they make more than £85,000 on goods and services subject to VAT exceeds in one tax year. If you don’t reimburse business mileage to your employees, you can’t claim the mileage allowance. If you don’t give loans to yourself as a company director, you are to pay nothing on it.
Corporation Tax
Corporation Tax is applied to limited company profits after business expenses have been paid, but before dividends are withdrawn. Speaking of the rate, for the 2019/20 tax year it is 19%.
VAT Rate & Threshold
Value Added Tax is charged on most goods and services in the UK.
| 2019/20 | |
|---|---|
| The Standard VAT rate (applicable to most goods and services) | 20% |
| The Reduced VAT rate rate (applicable to certain goods and services) | 5% |
| The Zero VAT rate (applicable to some goods and services (food, children’s clothes etc.) | 0% |
Mind that being subject to zero VAT rate and being exempt from VAT is not the same thing.
The VAT Registration threshold is the amount of revenue at which your company must register for Value Added Tax. This tax year, you must register for VAT within 30 days after your business sold goods and/or services that aren’t exempt from VAT for a total of £85,000. Both sole traders and limited companies are obliged to register for VAT once they pass this threshold or anticipate passing it in a single thirty-day period.
| 2019/20 | |
|---|---|
| The VAT Registration threshold | £85,000 |
On Flat Rate VAT scheme, companies use a predetermined VAT rate based on the industry type and pay the tax over to HMRC, while still charging customers full 20%. However, you can’t reclaim you can’t reclaim the VAT on most of your purchases.
See the full list of industry-specific VAT flat rates
Mileage Allowances
If you and/or employees use vehicles for business purposes (deliver flowers, drive to another city to meet the new partner, etc.), you can count how many miles you travel and claim those rides to be business expenses. Thus, some money will be deducted from your taxable income and you will pay less corporation tax.
HMRC has determined how much money you can claim per mile. This is called the approved mileage allowance payments (AMAP). The rates depend on the vehicle type and on how big your mileage is:
| First 10,000 miles | Over 10,000 miles | |
|---|---|---|
| Car / van | £0.45 | £0.25 |
| Motorcycle | £0.24 | £0.24 |
| Bicycle | £0.20 | £0.20 |
Director Loan Rate
Your limited company can loan money to you. In case you are surprised, we described the whole scheme in a separate article.
If at some point throughout the year the amount of money that you borrowed exceeds £10,000, you have to pay 2.5% nominal interest on the whole sum and also 13.8% of NIC. Also, you may need to report about the case on your form P11D — the one that deals with “benefits in kind”. To know for sure, please speak with your accountant.
Conclusion
We tried to provide some context for you to make sense of the taxes you are to pay and as well as the rates and thresholds that will affect you. However, the UK tax system is a complicated thing, so we couldn’t help but leave out some things. So we advise finding a thorough accountant who would guide you and your business through the tax season and explain all the nuances to you.
A mediocre accountant prepares and files his papers in silence — a great accountant advises you on legally reducing your tax liability and makes sure you have answers to all your questions. We wish you to find such a professional.
Take care and good luck!
Incorporate your UK company with us! Our experts will be in charge of the routine, while you'll be doing what's really important.