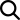How Electronic Signatures Work in Singapore
Many businessmen live with reams of papers all over the office — although they don’t have to. In Singapore, most documents can be signed on the computer, which is just as legal. Let's see how electronic signatures work, consider the requirements and restrictions according to digital signature Singapore law, and learn how to secure electronic communication.
By the way did you know that our company secretaries sign everything electronically? Check out our secretarial services in Singapore to see for yourself!
What requirements for e-signatures are there?
Why choose an e-signature?
What is the difference between an electronic and a digital signature?
How do I get a digital signature?
How can I use an e-signature in my business?
What software do I need to use an e-signature?
In what cases is the use of an e-signature forbidden?
To sum up
What can an electronic signature look like?
An electronic signature (e-signature) is a digital alternative to the handwritten signature. It helps you sign documents online without printing them.
An e-signature doesn’t always look like a copy of your handwriting on the screen. According to the Electronic Transactions Act, it can take any form like:
A sender’s name typed in an email. Most of us are using this type of signing every day without realizing it to be an e-signature. Suppose you make an offer to a client in an email or approve an absence note of your employee. You just send a message from your corporate account and sign your name. You can also use it in communication with a contractor. However, we recommend stipulating in an original contract that any information and agreements expressed from certain emails are legally binding. This way, you can enforce the deal and ensure that only responsible persons can influence the agreement. Example of an e-signature clause in a contract:
A scanned copy of a handwritten signature. You can just sign a piece of paper, scan it or take a photo, copy and paste the image to the document. On the screen, it looks exactly like your handwriting. For example, this method is commonly used for in-house corporate paperwork, for employment offers, and online services like insurance.

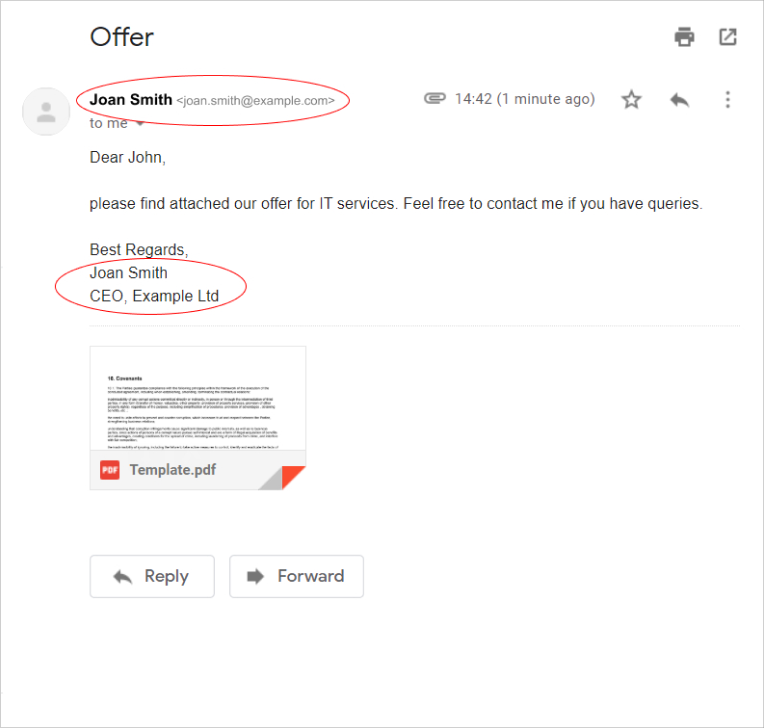
A drawing of a signature made with a mouse, a touchscreen or trackpad. You can paste the said drawing into the document. Some companies, like delivery services, integrate the drawing function into their customer programs. The courier delivers items and gives a tablet to the client to sign the screen, confirming the delivery.
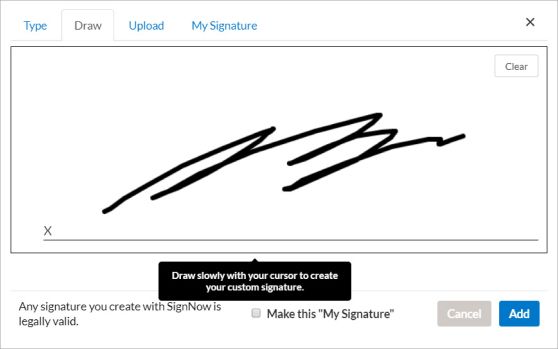
A click of an acceptance button. This method is usually used in public offers for online shopping. For instance, if you sell clothes or books online, you can put terms and conditions on your website and an “Accept” button for customers to agree.
A password or any other code. If you provide services, you can develop user accounts for your clients like in online banking. Customers can access their personal information, securely communicate with you or even carry out payments. Password identification least of all looks like signing in the conventional sense, but it still has the same goal and legal effect.
A biometric identifier like a fingerprint, a voiceprint or a retinal scan. Fingerprints and face readers are broadly used on modern smartphones to get access to a phone, to agree with terms or to proceed payments. Consider this method if you develop an app for your business.
A digital signature. This is an encrypted code which is as secure as personal handwriting. A digital signature is usually used for filing forms with state authorities and for major deals. Find more information below.
The list goes on.
What requirements for e-signatures are there?
Any e-signature method is appropriate if it identifies a person and clearly indicates his or her intention towards the signed document. At the same time, it must be reliable and appropriate for the purpose of the document or give proof of identification and original intention. Let's look closer at these requirements:
Identification. When signing a document, make sure to write your name, the date, and your company’s information. Otherwise, the signature turns into a valueless symbol on the screen. In corporate communication, avoid the use of nicknames or personal unidentified email addresses like dragonmaster@gmail.com.
Intention. A handwritten signature presumes that the signer personally read and agreed to these particular terms. The same goes for using an e-signature. Taking into account the context, the content of the document must be clearly connected with the signature. For example, you attach the signature to the document you want to sign instead of sending it separately referring to the agreement you made with a partner earlier.
It is also better not to rely on automatic systems like auto-replies or fax. The machine automatically adds the data and sends the message. It is not personally approved by the sender and it will be hard to prove the intent of signing, without which the signature is not legally binding.
Reliability and appropriateness. Obviously there are different approaches for minor and major deals. Not all signatures are highly secured, but not every case requires them to be. Accepting a scanned signature for buying a dozen of USB-sticks is fine, but for purchasing 10 Lamborghinis you’d better stick with a secured digital signature.
Why choose an e-signature over a hard copy signature?
An e-signature is designed to simplify and improve operational business efficiency. It has various benefits in comparison with traditional handwriting:
- Saving costs. Buying paper and supplies, printing, paying for postage and file storage may cost you a fortune. The electronic process only requires a computer and a signature itself. Though using high-security methods can be pricey, investing in the electronic signature will pay off soon.
- Saving time. You don’t have to meet up with your business partners to sign documents or to wait for the post to come. Instead, you can momentarily sign and send a document via email or any other online system, and it will reach the proper addressee.
- Reducing the risk of human errors. You are less likely to confuse the final version of a document with an interim one or sign the wrong contract.
- Ensuring security. With an e-signature, you can track who, when and where has signed the document. It is especially useful as evidence when it comes to complaints and litigation.
- Automating processes. Electronic documents are easier to sort and collect.
- Attracting new customers. With e-signatures, your customers can make a purchase or file an application straight away via a smartphone or a laptop. You’ll have an advantage over your competitors.
- Helping the environment. By saving paper you save trees.
What is the difference between an electronic and a digital signature?
A digital signature is the most secure kind of electronic signature and is definitely more than a click. It contains the user’s encrypted data and protects the documents against unauthorized changes.
Put simply, it is a mathematical formula that makes a connection between the content of the document and a person’s secret key. A signer has a private key like a personal code granting him the right to create a signature. On the other hand, the recipient of the document uses a public key to verify the digital signature.
On your end, it goes like this: you get a certificate once and use the same USB token every time you need to sign a document. With a couple of clicks, you e-sign the file. The signed document can be sent by email; email service can tell if the message is digitally signed, who signed it, and whether the signature is valid.

How do I get a digital signature?
To use a digital signature, you need a digital certificate and a secret key. For safety reasons, the key is usually stored in a device like a smartcard or a USB token.
Only a licensed Certification Authority (CA) can issue a digital certificate and a private key. CAs are not really state authorities, they are licensed private companies. Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) licenses CAs and releases the list of accredited companies. For now, only one CA has accreditation. It provides both certificates and technical support.
There are two different kinds of certificates: for personal use and for company use. The CA verifies a person’s or company’s identity, so you have to fill in an application and provide certain documents like a personal ID, a business profile from ACRA and a letter of authorisation for a company to appoint you as a responsible person. The CA may also request additional information. The price for a certificate and a USB token differs and is approximately S$120-180. Technical support is charged additionally.
How can I use an e-signature in my business?
There are various possibilities to use an e-signature in Singapore:
With authorities. Communication with state authorities in Singapore involves a lot of electronic documents exchange. Corporate Pass (CorpPass) is a unique digital identity for inland and foreign companies to transact online with Government agencies. Some transactions like filing tax returns may also require a digital signature.
With partners and customers. Contracts with an e-signature are legally valid and enforceable under the law in Singapore as long as they correspond to the general contract law.
For in-house corporate issues. The Board of Directors may approve meeting resolutions or produce any other note by means of a digital signature, as well as HR documents including employment contracts and NDAs.
What software do I need to use an e-signature?
The software you will need depends on the type of a signature that you choose. We will not give recommendations on software for passwords creation or biometric identification, as you need web developers and builders for the purpose. Let's concentrate on the more common examples.
You can add an image of a signature to documents in most editorial programs using “copy and paste”. For every operating system, there are programs that let you add scanned signatures, drawings and digital signatures.
If a computer is out of reach, you can create a signature on the go with your smartphone. There are apps like Draw Signature Pro or Autograph+ allowing you to draw, to save an image on a transparent background and optionally to enhance and smooth your image.
If you often use e-signatures, consider buying a program that allows all-in-one to create a document, to add an e-signature, to manage tools, to make templates, to send documents, to automate a workflow or to be integrated into web-sites, applications, CRMs and payment tools. It could be PandaDoc, DocuSign, Adobe Sign, ESignGenie, EmSigner, or some other program. Please do not consider any reference to a program or an app an advertisement. We list them as mere examples.
In what cases is the use of an e-signature forbidden?
The Electronic Transactions Act provides an explicit list of documents that are not allowed to be signed electronically. It excludes, for example:
- wills,
- documents that appoint a beneficiary or claim the delivery of goods and the payment of a sum of money,
- powers of attorney,
- legal actions involving real estate.
Additionally, even if the law allows the use of an e-signature, you can agree with the other party to exclude it as well as any electronic communication or record. Just indicate it in a contract.
What if someone wrongfully uses my e-signature?
First of all, to avoid the situation, never give anyone access to your email, passcodes, identification details or a private key to your digital signature. Instead, you can trust anybody with the right to act in your or your company’s name by issuing a power of attorney.
If the worst has happened and someone fraudulently signed an electronic document using your data, you have to inform the recipient, file a claim to the police and collect evidence. For example, you can always trace the date and the place of signing and prove you weren’t there at the time. Should your digital signature be compromised or you lose a private key, report it to the CA immediately. The authority will suspend or revoke the certificate.
To sum up:
- In Singapore, an e-signature is legal, enforceable, and court-admissible.
- An e-signature can be anything from a mouse click to a secured algorithm provided that identifies a person, indicates his or her intention and is appropriate.
- An e-signature improves companies’ operational business efficiency.
- A digital signature is a kind of electronic signature that provides secure validation and authentication. You can get a certificate from the Certification Authority.
- You can use an e-signature for communication with the authorities, for concluding contracts or corporate transactions. However, it can’t be used for wills, negotiable instruments, powers of attorney or real estate transactions.
- To avoid the use of an e-signature by a partner, specify so in a contract.
- Don’t share access to your personal e-signatures.
- Contact involved parties and authorities as soon as possible if someone fraudulently uses your e-signature.